Lynch Syndrome Lung Cancer
Lynch syndrome lung cancer. Lynch syndrome also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC is caused by mutations in any of several genes that impact cells ability to repair damage to DNA. In addition membranous programmed death ligand-1 PD-L1 tends to be expressed at higher levels in MSI-H cancers than in microsatellite-stable cancers. People affected by LS have a higher risk of developing some types of cancer including cancer of the.
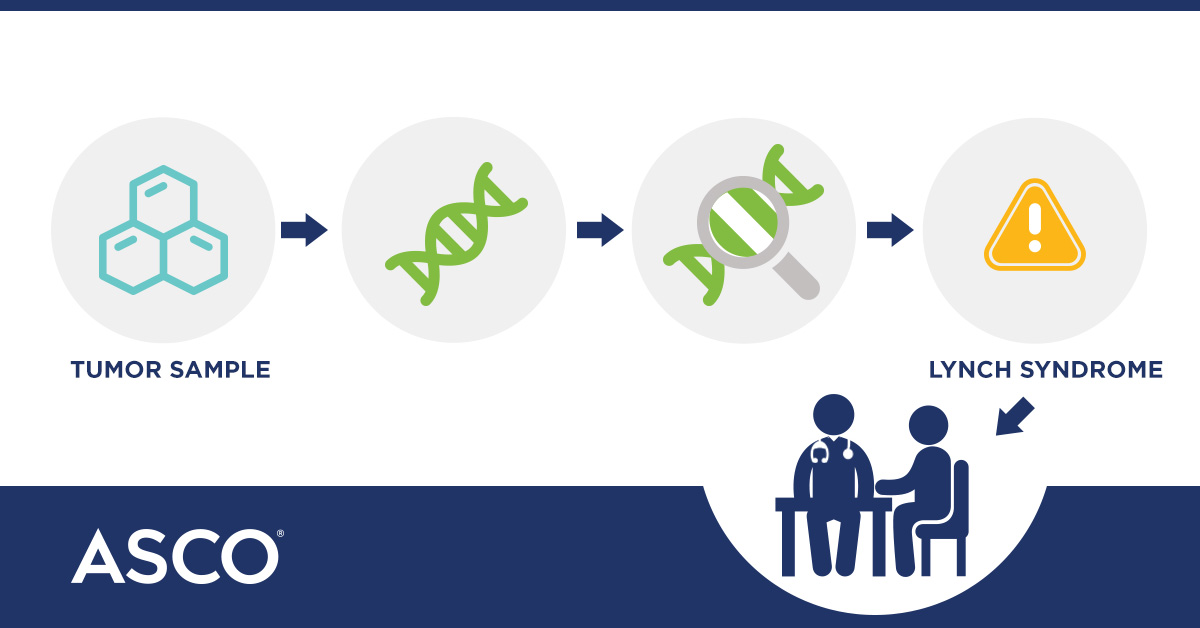
What is Lynch syndrome. The spectrum of cancers seen in a hospital based Lynch syndrome registry of mismatch repair gene mutation carriers was examined to determine the distribution of cancers and examine excess cancer risk. A main reason why it is important to know if a person diagnosed with cancer has Lynch syndrome is because his or her family members may also have the syndrome.
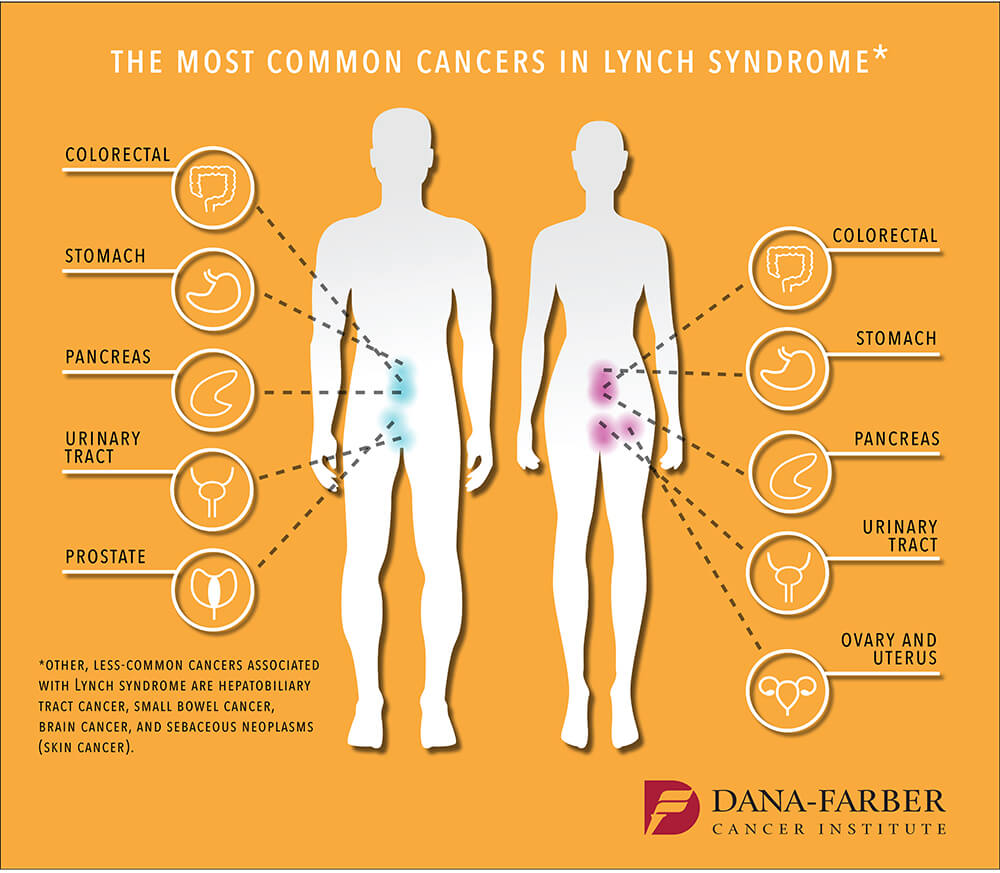
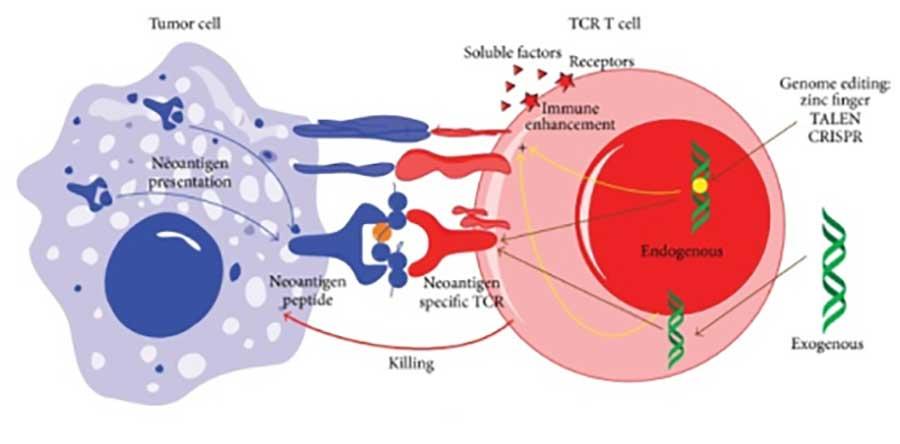
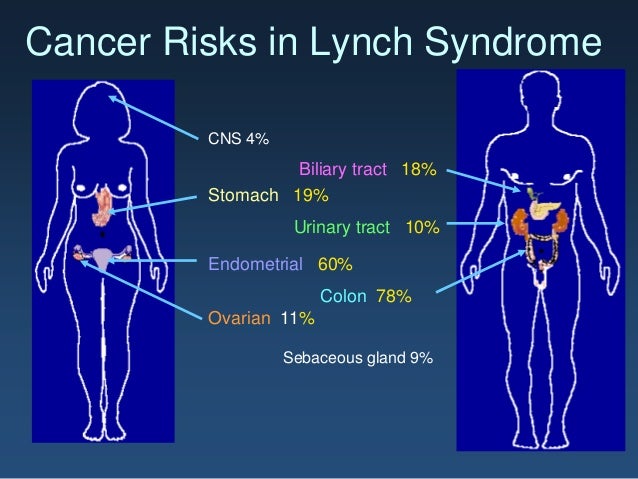
Colorectal cancer and uterine endometrial cancer are the two cancers a person with Lynch syndrome is at greatest risk to develop. An increased number of mutation-associated neoantigens have been observed in patients with high-frequency MSI MSI-H cancer. It used to be called hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC.
However the risk of developing cancer is higher than for people who do not have Lynch syndrome. Lynch syndrome also known as hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC is the most common cause of hereditary colorectal colon cancer. A genetic syndrome that could influence a persons likelihood of developing pancreatic cancer as well as other cancer types like colon cancer is called Lynch syndrome.
People with Lynch syndrome also have an increased risk of cancers of the stomach small intestine liver gallbladder ducts urinary tract brain and skin. Extrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer. Overall there were 504 cancers recorded in 368 mutation carriers from 176 families.
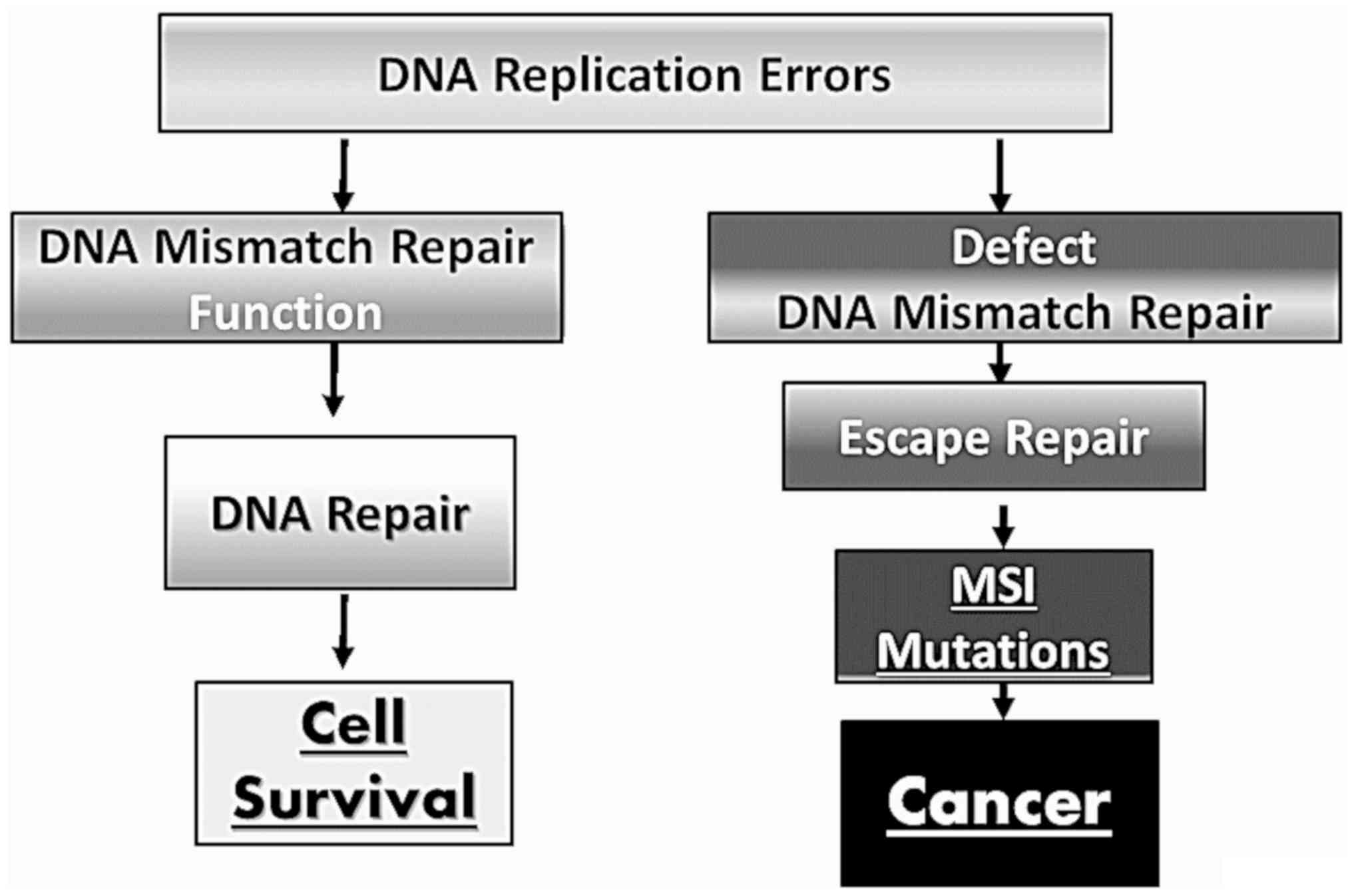
According to researchers the risk of colorectal cancer in individuals with Lynch Syndrome can vary substantially depending on both gender and the. This means people with Lynch syndrome have a higher risk of certain types of cancer. Lynch syndrome is caused due to the mutation in the DNA repairing genes thus increasing the risk of various cancers and the highest risk is of colorectal cancer.
The level of risk of developing cancer depends on which mismatch repair genes are faulty. Cancer begins when normal cells begin to change and grow out of control.
The spectrum of cancers seen in a hospital based Lynch syndrome registry of mismatch repair gene mutation carriers was examined to determine the distribution of cancers and examine excess cancer risk.
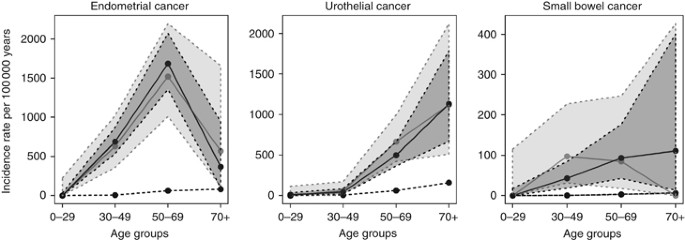
Overall there were 504 cancers recorded in 368 mutation carriers from 176 families. Extrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer. A main reason why it is important to know if a person diagnosed with cancer has Lynch syndrome is because his or her family members may also have the syndrome. A genetic syndrome that could influence a persons likelihood of developing pancreatic cancer as well as other cancer types like colon cancer is called Lynch syndrome. Lynch syndrome is caused due to the mutation in the DNA repairing genes thus increasing the risk of various cancers and the highest risk is of colorectal cancer. Lynch syndrome is a hereditary condition that makes a person more likely to develop cancer. In addition these genetic features can spontaneously occur in tumors and have been found in patients with several cancer typesmost commonly colorectal endometrial and gastrointestinal cancers. 16-18 One case was the Muir-Torre variant of Lynch syndrome with the loss of MSH2 expression 16 and the second was a germline variant in MSH2 in which the tumor was immunohistochemically deficient for MSH2 and MSH6 with MSI-high. Tumors that are dMMR and MSI-H are found in patients with Lynch syndrome a genetic disorder caused by mutations in genes that control DNA mismatch repair.
The spectrum of cancers seen in a hospital based Lynch syndrome registry of mismatch repair gene mutation carriers was examined to determine the distribution of cancers and examine excess cancer risk. In addition membranous programmed death ligand-1 PD-L1 tends to be expressed at higher levels in MSI-H cancers than in microsatellite-stable cancers. An increased number of mutation-associated neoantigens have been observed in patients with high-frequency MSI MSI-H cancer. The level of risk of developing cancer depends on which mismatch repair genes are faulty. Other names for Lynch syndrome include Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer syndrome HNPCC and Muir-Torre syndrome. Todays key research highlights address the connection between microsatellite instability and Lynch syndrome a blood test that may be used to find early lung cancer a new targeted therapy for treating advanced breast cancer an immunotherapy-chemotherapy combination that slows lung cancer growth and evidence that personalized medicine helps people with cancer live longer. Tumors that are dMMR and MSI-H are found in patients with Lynch syndrome a genetic disorder caused by mutations in genes that control DNA mismatch repair.

























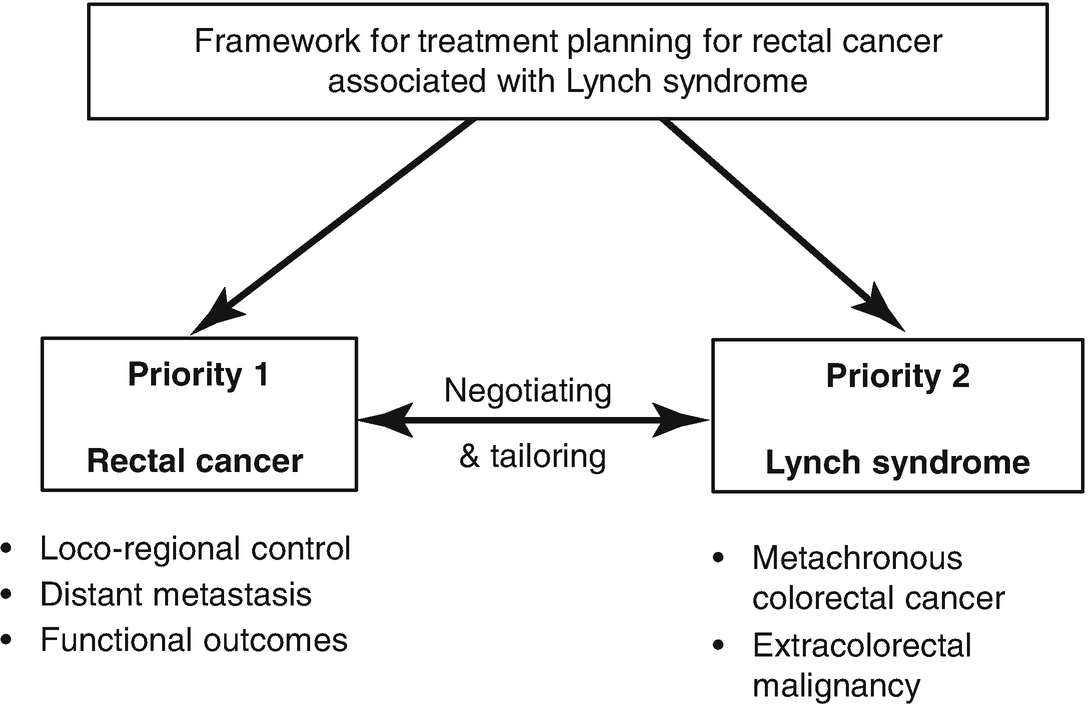




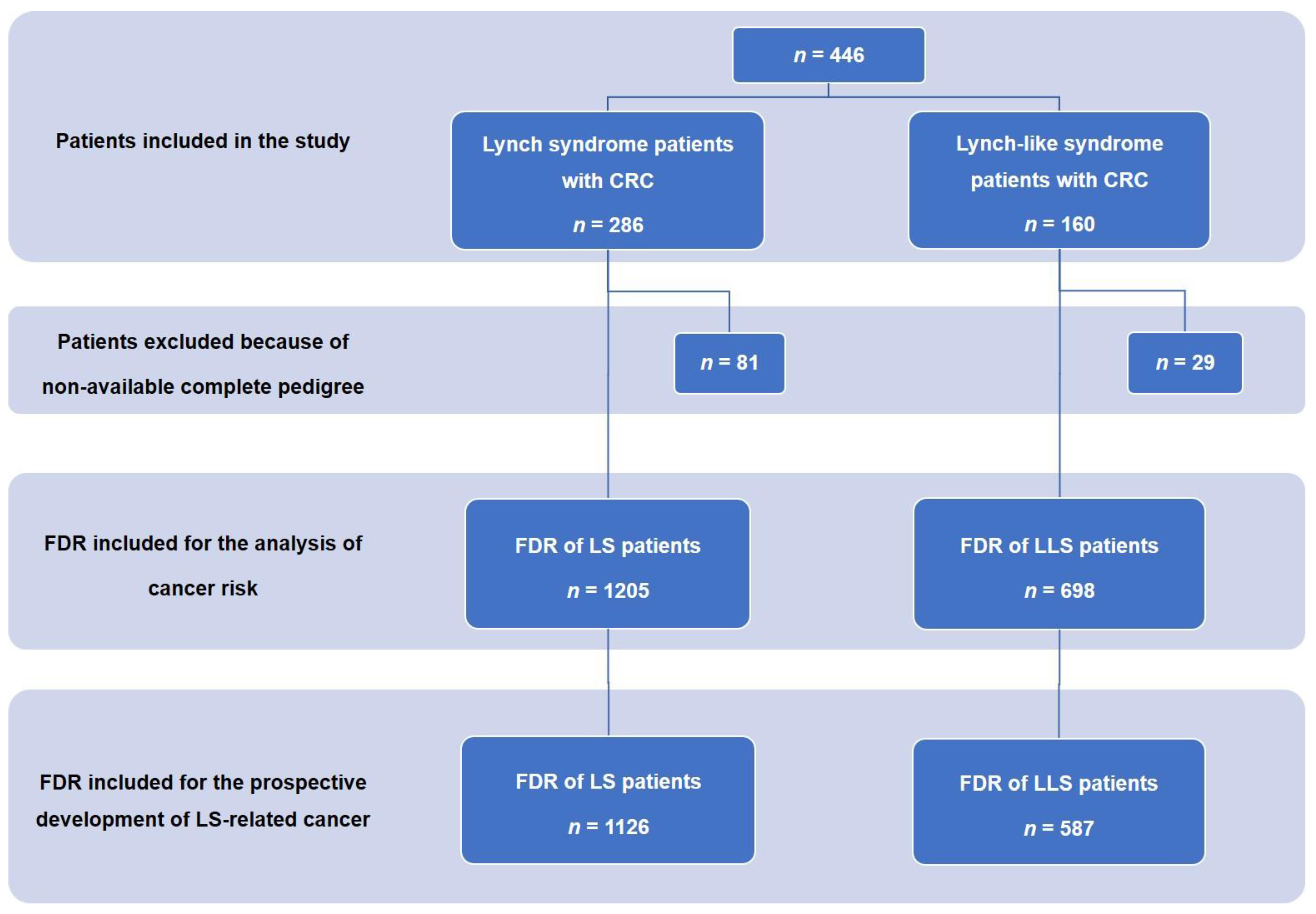



Posting Komentar untuk "Lynch Syndrome Lung Cancer"